Server side tagging may have come across a scenario when you visit a website and it immediately presents you with advertisements or content that seems to fit your interests or recent activities.
This has been done in the past through tag management with the use of tags that are placed on the client-side, that is, on the actual HTML of the site. However, there’s a new sheriff in town: Server side tagging.
What is server side tagging?
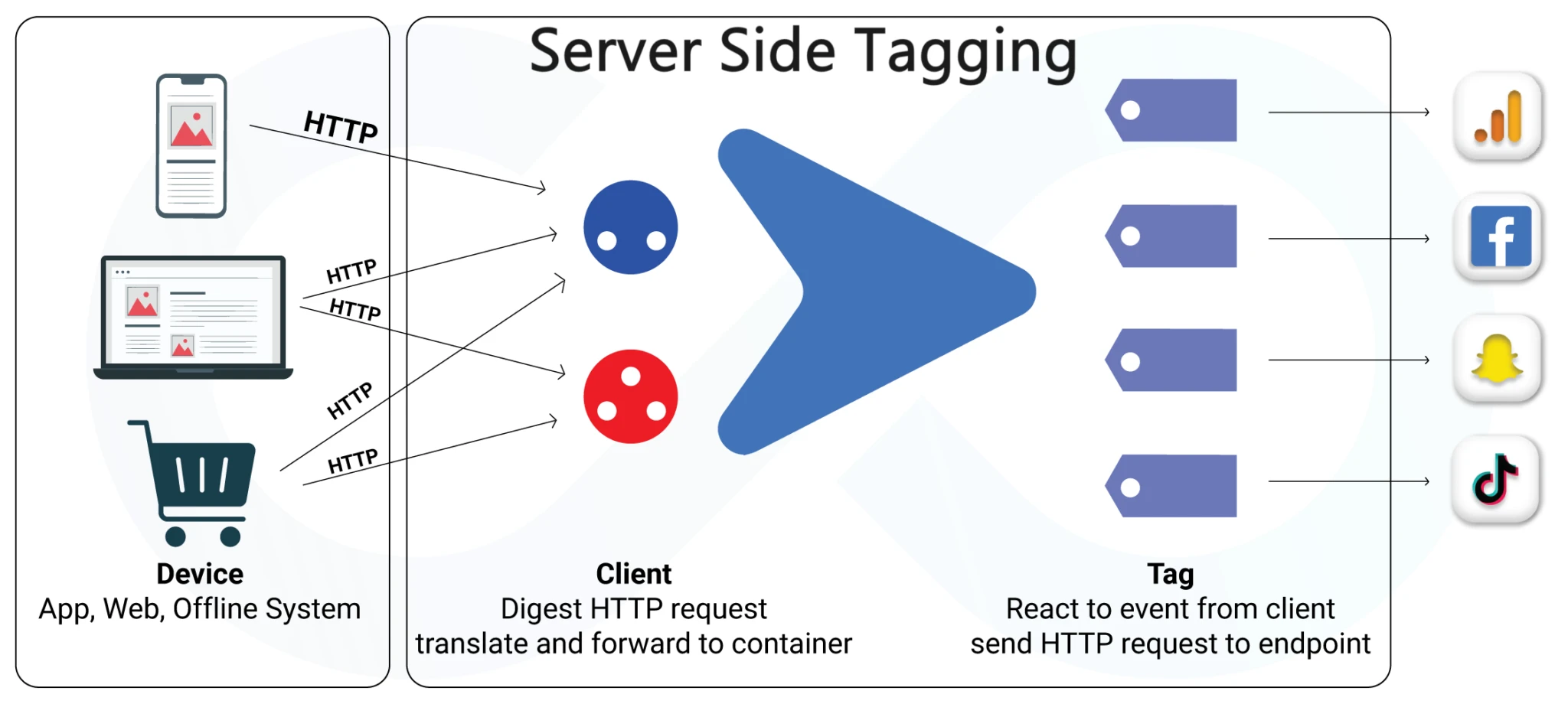
Server-side tagging (SST) is a relatively new idea in the field of digital marketing that presents a method of shifting the deployment of tracking tags to the server side.
This is in contrast to traditional client side tagging where the tags are run in the browsers and which results into increased dependence on the device of the user, leading to compromised quality, safety and efficiency of the data.
This method is gradually becoming popular, and companies are embracing SST to avoid the dangers of data privacy, ad blockers, and browser limitations.
Google Tag Manager: Server Side Tagging
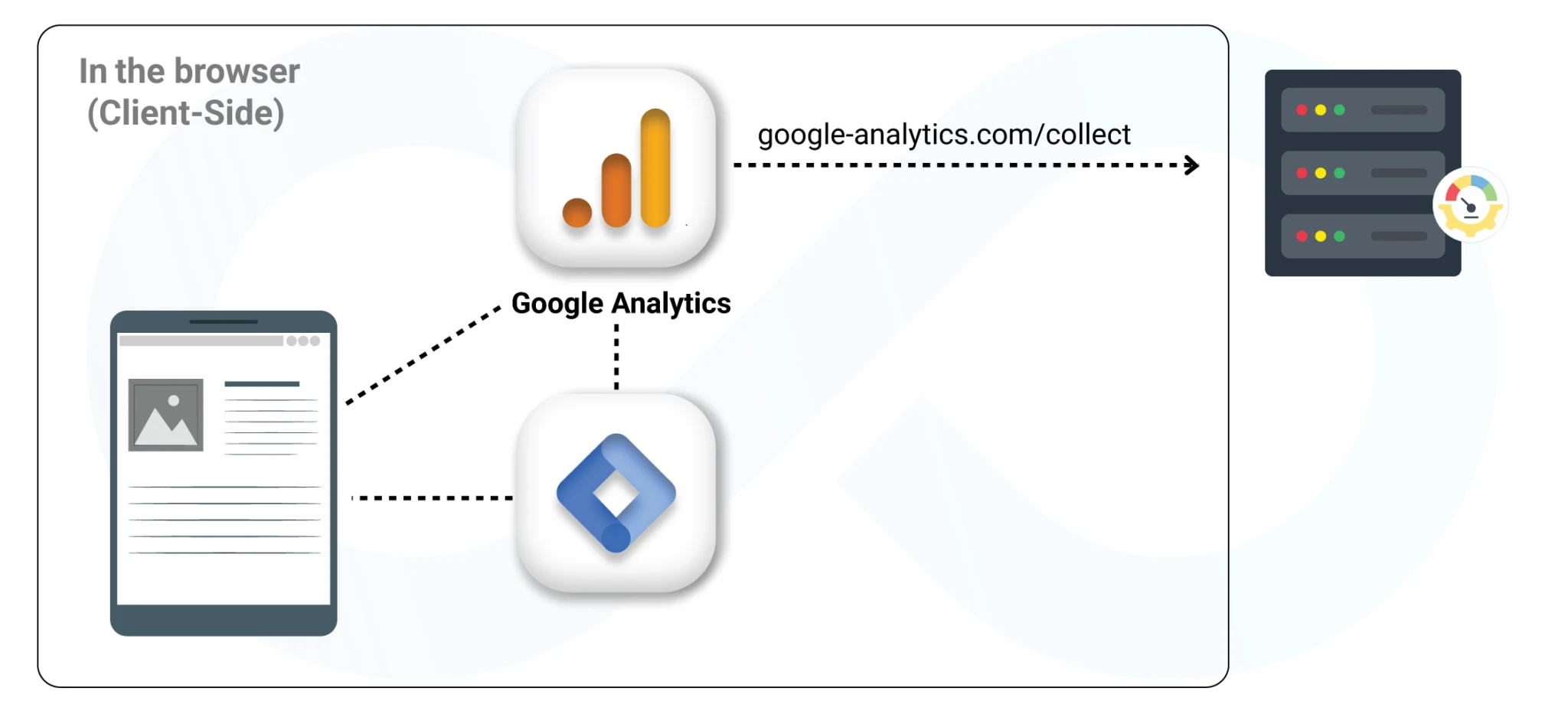
Currently, Google has enhanced the features of Google Tag Manager (GTM) through the incorporation of Server Side Tagging that allows organizations to place tracking tags within a server context.
The latest developments reveal that more than 50% of marketers have adopted server-side tags for the specific goal of making the dependability and security of data accumulation more reliable.
Server-side tagging in GTM enables installing and tracking tags on the side of the server, which is helpful in preventing an overload at the client side and in selecting only the data required by the third-party platforms and passing through the validation.
This setup has received considerable attention as organizations look for the best ways of protecting and handling consumer data because of the nuances such as GDPR and CCPA.
Server side tagging vs server-side tracking:
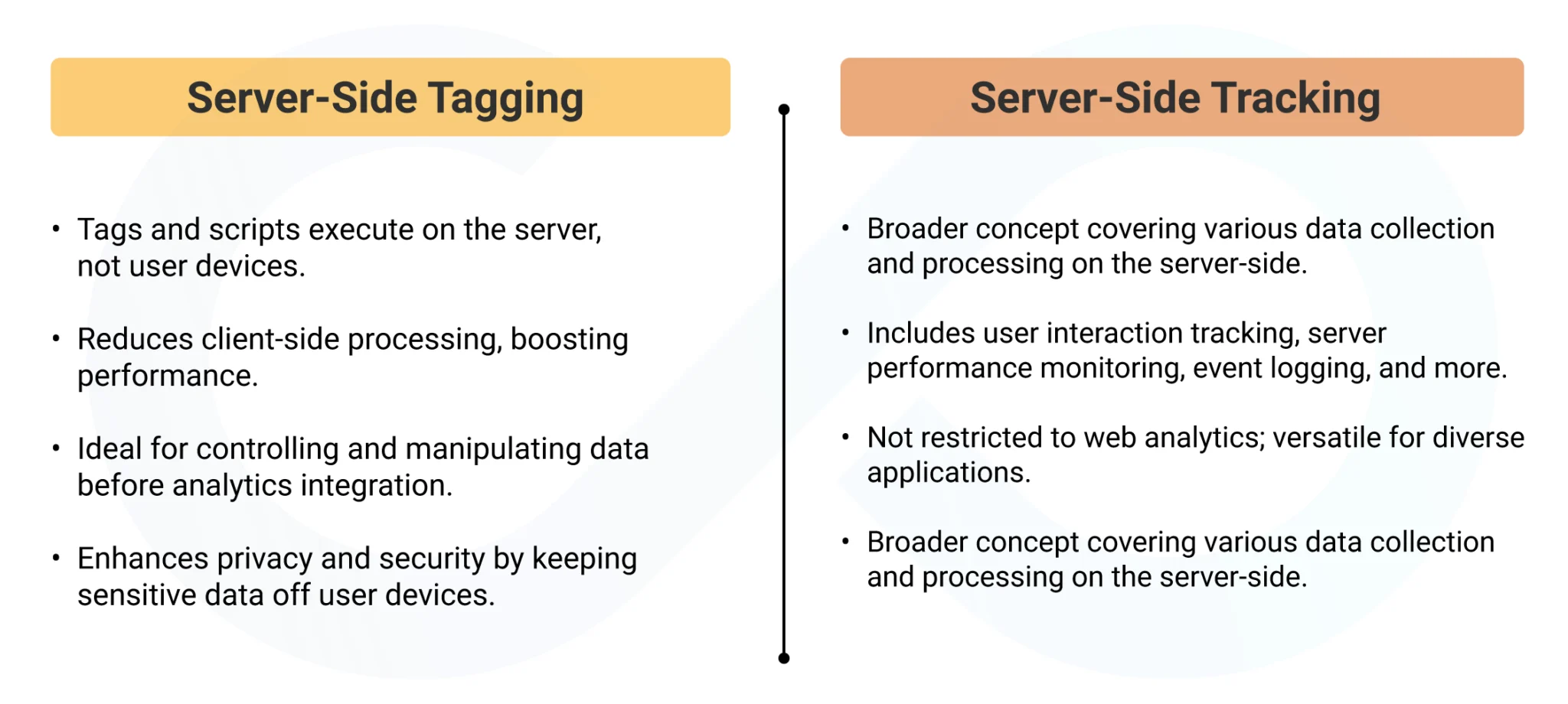
Arguably, server-side tagging and server-side tracking are now days used interchangeably due to similar naming conventions but in reality, they are deployed for different uses in the universe of data management.
One major difference lies within the execution and management of tags: server-side tagging puts tag executions and management on the server side, which offers more control over the collected data.
On the other hand, server-side can be defined as the process where user interaction information is conveyed to analytics platforms, disseminating the information at the server level, without involving the user’s browser. Research shows that when server-side tracking is used, audiences measurement accuracy can be higher by up to 30 percent relative to the client-side approaches.
This approach has the goals of enhancing the quality of data aside from the protection of privacy, however, it differs from the main approach in that it is used in different circumstances depending on the requirements of a business.
Google Analytics with Server-Side Tagging:
The place of server-side tagging in Google Analytics is very beneficial because it provides many significant advantages like increased security and data compliance.
Server-side tagging can also help to prevent errors caused by browser restrictions such as ad blockers and JavaScript issues by only sending clean and pre-approved data to Google Analytics. Some of the studies indicate that organizations engaging in service side tagging experience increased precision in their analysis data up to 20%.
This approach also assists organizations to adhere with high data privacy regulation throughout regulating the kind of information disclosed to third party service providers while protecting other users’ sensitive data from disclosure.
Benefits of Server-Side Tagging Over Client-Side Tagging
- Improved Data Accuracy: Server-side tagging helps to reduce the effect of blocking ads and restrictions in browsers, and thus leads to more reliable information collection, helped by the reported increased range of 15-25% of lost data.
- Enhanced Performance: Server-side tagging shifts tags’ execution to a server which can improve website performance, thus minimizing the time that websites take to load and directed towards a better user experience.
- Increased Security: This approach is useful because it configures the data transmitting process on the server side, minimizing the chance of compromising the information that appears in the user’s browser.
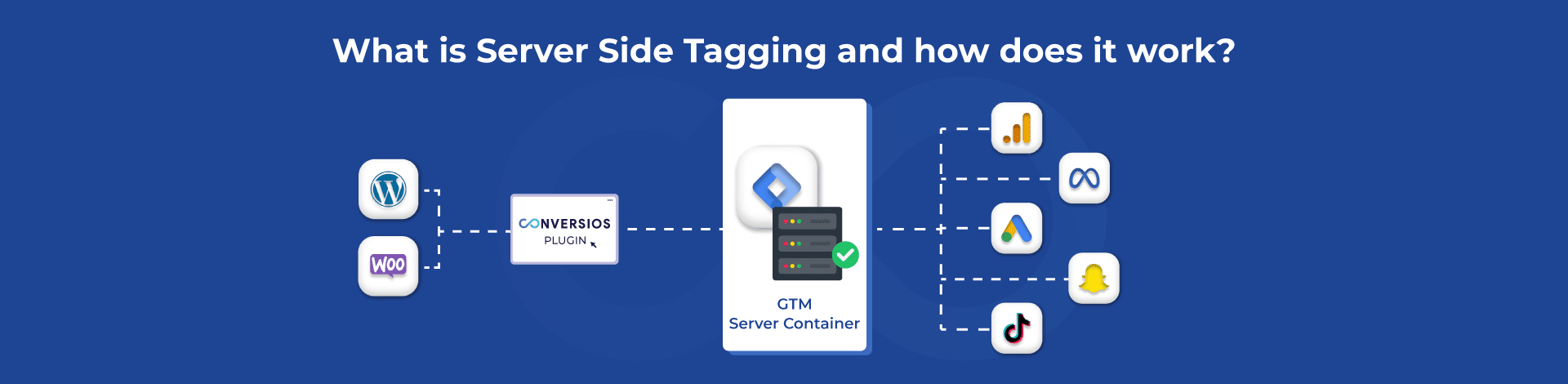
How Server-Side Tagging Works:
- Server-Side Tagging works by moving the tag computation to a separate server where it is executed instead of on the browser.
- A user visits a website he/she is interested in as it is associated with an event.
- This is better than loading a number of third-party scripts into the browser, which will then require a number of requests to the tagging server.
- This request is handled by the tagging server, with the execution of relevant tags and changes.
- The server further passes the processed data to various marketing and analytical tools as seen in the context below.
- Last of all, it hands back any information required by the user to the browser.
- This approach offers better coordination in data processing since it is function-centric, decreasing control complexities of data flows.
Rememeber,
Server-side tagging is a groundbreaking development in terms of how businesses approach their track and analyze operation. While moving the handling of tags from the client side within the user’s browser to the server side offering more security or robustness, server side tagging also improves data quality and website optimization.
Server-side Tagging and google tag manager is a trending topic and many organizations have started to implement it to manage the rising demands for data anonymity and security.
In an ever-changing digital marketing mix, server side tagging proves to be a significant question that businesses need to answer if they are keen on being strategic players in an era that is characterized by complicated and strict data compliances and a business climate where reliable data is core.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is server-side tagging?
Server-side tagging is a method of managing and executing tracking tags on a server rather than the user’s browser. It enhances data accuracy, improves website performance, and offers better security and privacy compliance.
Q. How does server-side tagging work?
When a user visits a website, tracking events are processed on a dedicated tagging server. This server validates and forwards the necessary data to marketing tools like Google Analytics, ensuring fewer data losses and improved control.
Q. What is the difference between server-side tagging and server-side tracking?
Server-side tagging focuses on managing tags on the server, while server-side tracking refers to sending interaction data from the server to analytics platforms. Though related, tagging controls execution; tracking controls transmission.
Q. What are the benefits of server-side tagging over client-side tagging?
Benefits include improved data accuracy (15–25% less data loss), enhanced site speed by reducing browser scripts, and better compliance with privacy laws through secure, server-side data handling.
Q. How is Google Tag Manager involved in server-side tagging?
Google Tag Manager now supports server-side tagging, allowing businesses to deploy tags in a controlled server environment. This helps prevent browser-based disruptions and ensures cleaner, validated data is sent to platforms like GA4.