Accurate tracking is one of the biggest challenges for digital businesses in 2026. Browser privacy changes, ad blockers, frequent website updates, and complex user journeys often lead to missing or incorrect data in analytics platforms. This is why the Google Tag Manager data layer has become essential for reliable and future-proof measurement when you understand how Google Tag Manager works.
In this guide, you will learn what the data layer in Google Tag Manager is, why it is more reliable than HTML scraping, how it supports server-side tracking, and how automating the data layer helps ensure accurate reporting in Google Analytics 4 and advertising platforms.
What Is a Data Layer in Google Tag Manager
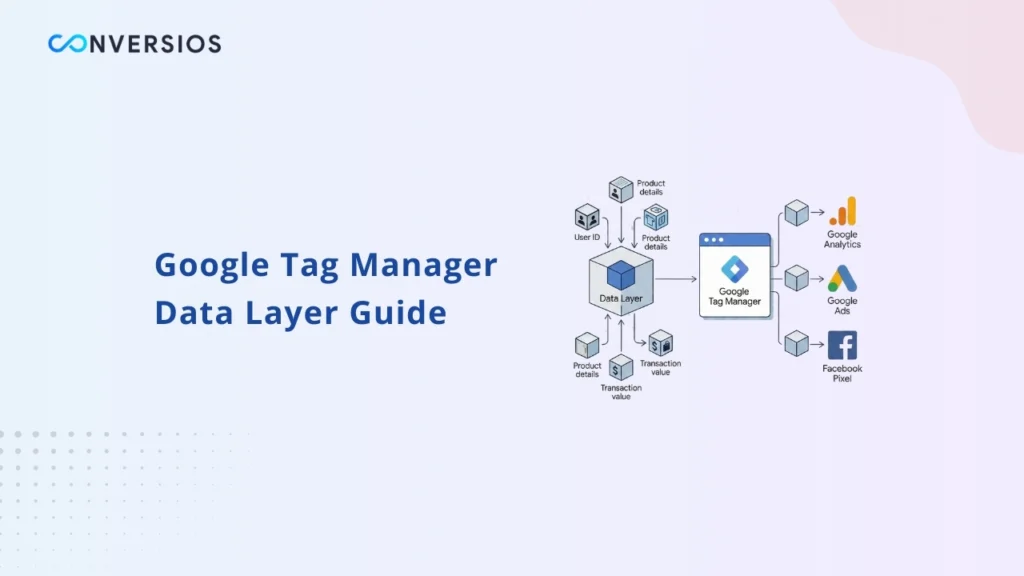
The data layer in Google Tag Manager is a structured JavaScript object that acts as a communication layer between a website or application and the tag management system. Instead of extracting values from visible page elements, the site pushes information directly into the data layer in a consistent format.
This information can include page details, user interactions, product data, transaction values, and event metadata. Google Tag Manager then reads this structured data and sends it to analytics and marketing tools.
For modern tracking setups, the data layer Google Tag Manager uses is the most reliable way to ensure clean, consistent, and reusable data across platforms. In 2026, relying on visual elements or page structure alone is no longer sufficient for accurate tracking.
Why the Data Layer Is Critical for Modern Tracking
Many tracking implementations still rely on HTML scraping, where tags read values from CSS selectors, DOM elements, or visible text on a page. While this may work initially, it is highly fragile.
Any change to the website layout, class names, or templates can break tracking instantly, leading to broken tracking issues.
This often results in missing conversions, incorrect revenue, or missing revenue in GA4, which you can diagnose using GA4 DebugView.
The data layer solves this problem by operating independently of the visual design. When a user performs an action, structured data is pushed into the data layer, and Google Tag Manager reads it directly.
Key advantages of using a data layer instead of scraping include:
- Stable tracking that does not depend on page design
- Consistent data across analytics and advertising platforms
- Fewer tracking issues after website updates or redesigns
Google Tag Manager Data Layer Variables Explained
Every value pushed into the data layer is accessed inside GTM as a Google Tag Manager data layer variable. These variables allow tags to dynamically retrieve values such as event names, prices, currencies, or identifiers.
Common examples of data layer variables include:
- event
- value
- currency
- transaction_id
- item_id
Using data layer variables ensures the same trusted data is reused across multiple tags, reducing discrepancies between analytics, ad platforms, and server-side integrations using GA4 event parameters.
Google Tag Manager Data Layer Example
A basic Google Tag Manager data layer example involves pushing structured data when a key user action occurs, such as a form submission, lead generation, or purchase.
A typical event push may include:
- The event name
- Relevant identifiers or IDs
- Monetary value and currency (if applicable)
- Contextual information about the action
Google Tag Manager listens for this event and triggers the appropriate tags. Because the data comes from the site’s logic rather than the page layout, it remains accurate even if the design changes.
The Role of the Data Layer in Server-Side Tracking
The data layer is the foundation of server side tracking. When tracking moves from the browser to a secure server environment, the server still needs a reliable and structured source of data.
The data layer provides this source. Events pushed into the data layer can be forwarded to a server container and then sent to analytics and advertising platforms using APIs once you validate server-side GTM.
With a clean data layer, server-side tracking helps:
- Reduce data loss caused by ad blockers
- Improve event and conversion accuracy
- Maintain control over how data is processed and shared
Without a properly implemented data layer, server-side tracking becomes difficult to manage and scale.
Why Automating the Data Layer Matters
Manually building and maintaining a data layer requires technical expertise and ongoing effort. Each new event, parameter, or tracking requirement introduces the risk of errors or inconsistencies.
Automating the data layer helps ensure that:
- Events are pushed consistently across the site
- Data structures follow analytics platform standards
- Updates do not break existing tracking
Automation also reduces dependency on custom scripts and simplifies long-term maintenance, especially as tracking requirements continue to evolve.
How to Test and Validate Your Data Layer
Implementing a data layer is only effective if it is tested regularly. Validation ensures that events fire correctly and that the values passed are accurate.
When validating a data layer, you should check:
- Whether events trigger at the correct time
- If values such as IDs, revenue, or quantities are correct
- Whether data layer variables populate consistently
Conversios provides a tracking checker tool that helps identify missing events, misfiring tags, and data inconsistencies. Regular validation ensures that reporting and optimization decisions are based on reliable data.
Conclusion
A properly configured Google Tag Manager data layer is essential for modern digital tracking. It replaces fragile HTML scraping, protects tracking from design changes, and enables advanced solutions like server-side tracking.
By automating the data layer and validating it regularly, businesses can reduce technical complexity, improve data accuracy, and confidently measure performance across analytics and advertising platforms in 2026.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is a data layer in Google Tag Manager?
A data layer is a structured JavaScript object that passes reliable information from a website to Google Tag Manager. It sends events and variables such as page actions, product data, and transaction values in a consistent format.
Q. Why is a data layer better than HTML scraping?
HTML scraping depends on page design and CSS selectors, which can break after website updates. A data layer works independently of design changes, making tracking more stable and accurate.
Q. Do I need a data layer for GA4 tracking?
Yes. GA4 relies on structured event data. A properly implemented data layer ensures correct event parameters, revenue values, and consistent reporting across platforms.
Q. How does the data layer support server-side tracking?
Server-side tracking requires clean input data. The data layer acts as the primary source of truth, allowing events to be forwarded from the browser to a secure server container and then sent to analytics and ad platforms.
Q. How can I check if my data layer is working correctly?
You can validate your setup by checking whether events fire correctly, values match real actions, and variables populate consistently. Tracking validation tools help identify missing or broken implementations.